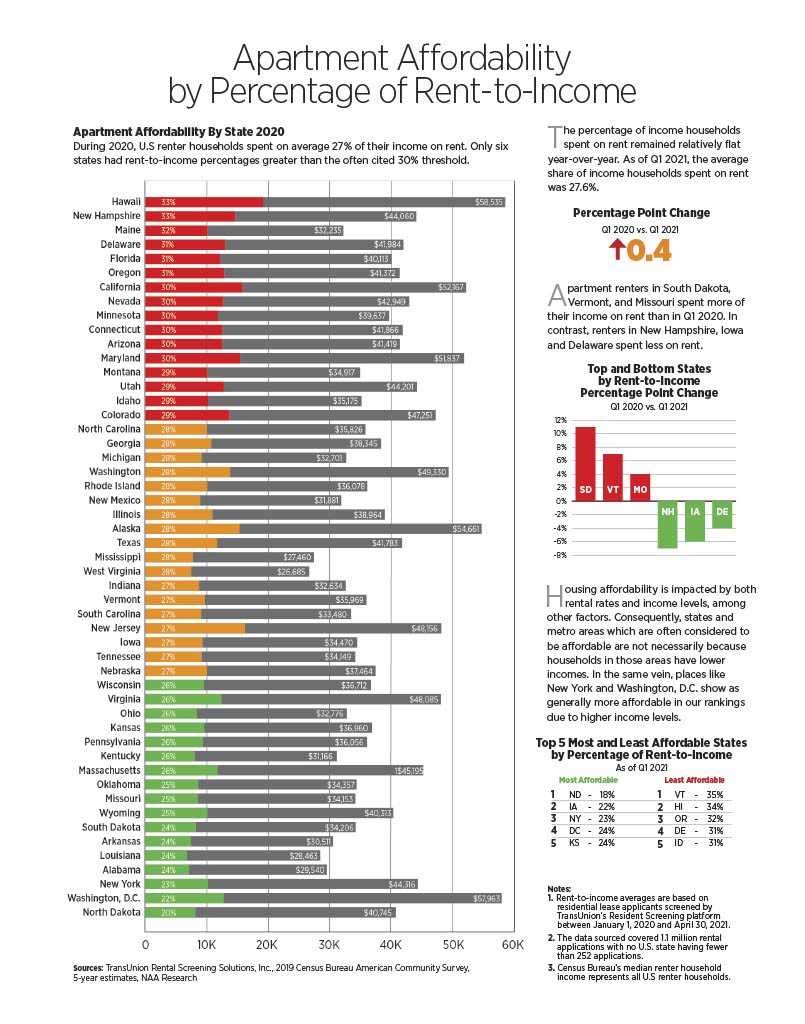
During 2020, U.S renter households in professionally managed properties spent on average 27% of their income on rent. Understandably, there is a broad variation in the share of income renters spend on rent at the state level. Primarily, income levels and rental rates are key contributing factors to rental housing affordability. States which are often considered to be affordable are not necessarily so because households in those areas have lower incomes. Likewise, states often viewed as costly are generally more affordable because of their high-income levels.
To assess rental housing affordability, NAA Research analyzed of rent-to-income percentages, which are based on residential lease applicants screened by TransUnion’s ResidentScreening platform between January 1, 2020 and April 30, 2021.
For more information, please contact:
